EPA Particulate Matter Rule Changes
Guest post by Clean Air’s spring intern Clover Kagle
On February 7th,the EPA released an update to guidelines regarding the annual emission limits of PM2.5 particles. The new annual limit of 9.0 µg/m3 is a decrease of 25% from the previous limit, 12.0 µg/m3. The EPA bases the decision on the health requirements in the Clean Air Act and the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS). The EPA claims the new guidelines will save over 4,500 lives over the next 8 years.
However, many agencies believe the stricter regulations do not go nearly far enough. The WHO has a recommended guideline of 5.0µg/m3, and many other countries already are enforcing this guideline. The EPA is not changing any secondary thresholds, PM10 thresholds, or 24-hour PM2.5 thresholds. The new limits do not affect most of the United States, with only 59 counties across the country needing to decrease their PM2.5 emissions to meet new guidelines.
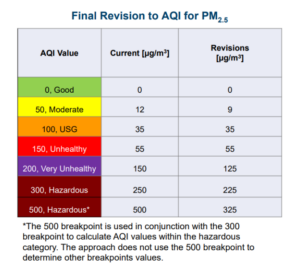
Another change in this decision is the air quality index levels. The EPA released the following graphic showing the revisions to health safety levels denoted by AQI – note that the threshold for “Moderate”, “Very Unhealthy”, and “Hazardous” are now lower than the prior thresholds.
RSS 2.0 feed. Both comments and pings are currently closed.